For manufacturers, keeping track of inventory and equipment is an essential part of daily processes. Lost inventory has a direct correlation with reduced profits, and misplaced equipment slows down operations in ways that can throttle fulfillment throughput and production efficiency. And legacy tracking systems are struggling to keep up with modern supply chain demands. So what are manufacturers doing to keep up? 91% manufacturing professional are familiar with barcoding systems to track goods and assets. But the technology that’s on the rise is RFID.
RFID technology is changing the world of manufacturing. Its improved accuracy and cost-effectiveness have sped up the adoption of this technology. According to a study by Zebra Technologies, over 90% of manufacturing companies plan to invest in RFID systems by 2028. This technology has the potential to improve operational processes and help companies meet the challenges they face in the fast-paced world.
How is RFID Deployed in Manufacturing Environments?
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology is fast becoming a cornerstone in modern manufacturing processes, revolutionizing the way products are produced, tracked, and managed. In manufacturing, RFID systems employ radio waves to communicate between tags attached to physical objects and RFID readers. This seamless exchange of information enables real-time tracking, monitoring, and control of assets, components, and finished products throughout the production cycle. By providing unparalleled visibility and automation, RFID enhances operational efficiency, minimizes errors, and enables precise inventory management. From streamlining supply chain logistics to optimizing inventory control, RFID technology has emerged as an indispensable tool in the quest for leaner, more agile, and highly efficient manufacturing operations across a diverse range of industries.
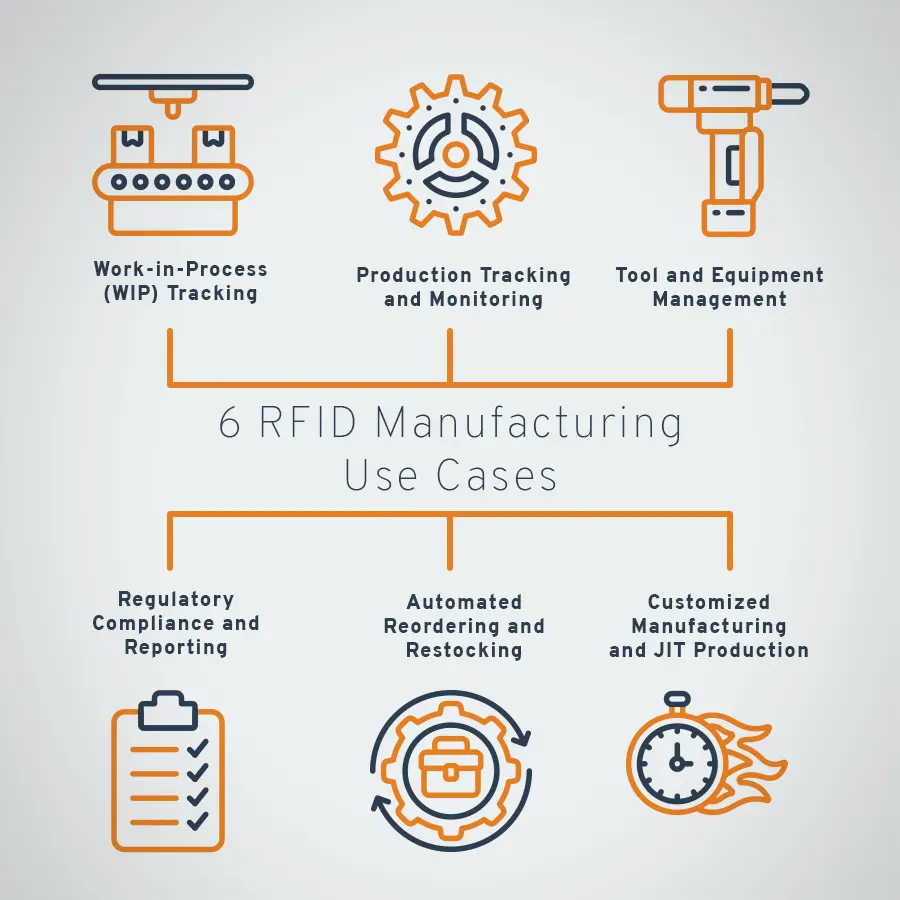
RFID Manufacturing Use Cases
RFID technology is transforming the landscape of modern manufacturing, offering a multitude of use cases that enhance efficiency, accuracy, and visibility in production processes. But an RFID system can do more than just detect inventory levels. Here are several key RFID manufacturing use cases:
Work-in-Process (WIP) Tracking
RFID facilitates the seamless tracking of goods as they undergo different stages of production – also known as WIP tracking. This ensures that each component receives the necessary processes, reducing errors and enhancing quality control measures.
Production Tracking and Monitoring
RFID tags are attached to products or components, allowing for real-time tracking as they move through various stages of production. This provides manufacturers with precise visibility into the status and location of each item, ensuring accurate production monitoring.
Tool and Equipment Management
RFID tags are affixed to tools and equipment, enabling manufacturers to track their usage, monitor maintenance schedules, and prevent loss or misplacement. This leads to optimized resource utilization and reduces downtime.
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
RFID systems assist manufacturers in automating compliance with industry-specific regulations and reporting requirements. Accurate and auditable records can be easily accessed to demonstrate adherence to legal standards.
Automated Reordering and Restocking
RFID-triggered alerts automate the reordering of materials when inventory levels fall below a specified threshold. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of production delays due to stockouts.
Customized Manufacturing and Just-in-Time Production
RFID-enabled systems support customized or build-to-order manufacturing processes by automatically configuring production lines based on specific product requirements. This enables manufacturers to meet unique customer demands efficiently.

The Benefits of RFID in Manufacturing
RFID is a great technology for managing manufacturing operations. It has the ability to improve accuracy, reduce cycle count time, improve traceability, and even reduce human error. These are just some of the benefits of RFID in manufacturing. Read on to learn more about the potential for RFID and the potential uses for your organization.
Improved Accuracy
In the business climate today, manufacturing is more challenging than ever before. Organizations are faced with multiple challenges, and the smart ones are turning to technology to improve inventory visibility. One of the biggest challenges manufacturers face is tracking spare parts and components, which are essential for efficient operations. Losing track of essential inventory is a business risk that can’t be taken lightly in today’s on-demand economy.
Using RFID to track products can improve security and prevent illegal product alteration. The technology also allows companies to track the purchasing habits of their customers, and can improve cost and performance across the entire supply chain. RFID is currently being used in the textile and apparel industries for a variety of reasons, including improving inventory management, tracking finished garments, and warehousing.
A major challenge for most organizations is tracking assets. This can include components that are on a production line, finished products being dispatched, industrial containers, tools, and other high-value equipment. RFID systems provide fast, reliable tracking of these assets. Unlike manual counting, RFID systems eliminate the need for costly human error in identifying and tracing individual assets.
RFID solutions can be integrated with ERP systems to create a holistic view of supply chain operations. They can connect multiple processes such as sales planning, assembly planning, and production scheduling. This allows companies to create plans that are consistent with their dynamic business processes. Combined, these three levels of planning can improve efficiency and ensure that finished products are delivered on time.
RFID technology also makes it easier to manage inventory. RFID readers can be strategically located around a warehouse to provide real-time visibility of inventory levels and prevent shrinkage. This helps companies minimize inventory and cut costs, while also keeping track of valuable assets.
Reduced Cycle Count Time
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify items. The data transmitted from an RFID tag to a reader allows companies to see real-time inventory information. This helps reduce out-of-stock situations and improve customer experience. RFID technology has the potential to significantly increase inventory accuracy, and can reduce cycle count times by up to 50% (According to GS1 US).
There are a variety of ways to implement RFID in manufacturing. The tags themselves can be passive or active. Active tags have a battery, while passive ones are powered only when scanned. In addition to tracking assets during production, RFID can also be used to validate inventory at key stages of production. This allows manufacturers to detect if inventory is off-schedule and prevent production delays.
RFID also can be used for inventory counts, as well as inbound/outbound checks. In addition to inventory counts, RFID can improve overall accuracy and allow companies to reorder at safety stock levels without the need for manual spot checks. Furthermore, RFID can be used to automate replenishment checks.
Another advantage of RFID is its ability to read a large number of items at once. Unlike a barcode scanner, RFID doesn’t require line-of-sight. This means that a counter doesn’t have to lift or see a box to count items. This greatly reduces the effort involved by the counter, which can improve the accuracy of counts.
Using RFID in retail can also increase customer experience. For example, by tracking inventory and quality data, retailers can ensure that the right merchandise is in the right place at the right time. RFID can eliminate the need to manually check individual packages or blind receipts, which can significantly reduce cycle count time. RFID can also be used to auto-reorder products to safety stock levels, which can help ensure maximum customer satisfaction. For example, a clothing company, Lululemon, uses RFID technology in its retail stores to improve inventory accuracy and the guest experience. They use RFID chips on hang tags to provide information about where an item is at any given time.
RFID technology has numerous other benefits for companies. It allows manufacturers to track inventory to the nearest few feet and eliminate manual searches. It also gives managers unprecedented visibility, allowing them to make better decisions. The data that RFID provides can also be fed back into the manufacturing process, ensuring better quality and efficiency.
Improved Traceability
RFID is a technology that allows for improved traceability of products and services across a manufacturing process. It offers tremendous benefits in areas like product genealogy and lifecycle traceability, inventory accuracy, kanban, and JIT environments. It also enables companies to improve their warehousing and yard management processes.
RFID can improve the efficiency of supply chain management by facilitating product integration and reducing costs. It can also enhance the productivity and quality of the goods. This means that an organization can achieve increased efficiencies and cash flow by making slight changes to its supply chain. However, there are some special considerations that should be addressed before adopting RFID in process industries.
Moreover, RFID provides end-to-end traceability, reducing gaps and enabling manufacturers to pinpoint problematic areas. Moreover, it helps identify damaged products in the production line, which is essential for passing audits. And, because of its reliability, it is also a cost-effective solution.
RFID solutions provide real-time asset tracking. A single RFID tag can track an asset from its production site all the way to the customer. This eliminates anxiety and frustrations related to delivery, which ultimately increases customer satisfaction. RFID also enables companies to track manufacturing tools and equipment. This helps them identify them easily, and it can be integrated into the production control systems to ensure a smooth and efficient workflow.
RFID technology is also a viable solution for the food industry. It makes it easier for businesses to manage inventory, reduce costs, and streamline processes. While traditional barcodes require humans to manually scan products, RFID automates this process and reduces the risk of duplicate orders. By tracking products throughout the entire process, manufacturers can maximize their productivity and reduce the amount of waste.
RFID technology is becoming more common in the manufacturing industry, and its use has been commercially available for over 30 years. Today, it is commonly used to track equipment, identify containers, and route materials in industrial environments. The benefits of RFID are most apparent in situations where traceability and accuracy are essential. Furthermore, RFID provides more information than barcodes do.
Reduced Human Error
One of the benefits of using RFID in manufacturing is the reduction of human error. The technology helps to identify an item’s location within seconds and is useful for managing inventory. This can eliminate the “search regret” effect and make processes easier and faster. Moreover, with the help of sophisticated inventory management software, RFID systems can be linked with real-time production tracking at the production facility.
RFID is an automatic identification system that includes tags and reader devices. Other components include tag servers, middleware, and application software. The tag itself contains a radio-frequency antenna and a small chip with an embedded barcode. The reader, on the other hand, collects and processes the information.
In manufacturing, human error is a major issue. Humans can make mistakes that can cripple the entire system. Human error can cause a multitude of problems, including misplaced materials, contaminated products, and skipped process steps. As a result, human errors can lead to lost business, product recalls, and even potential end-user risks. Reduced human error can help manufacturing companies achieve a competitive advantage.
RFID is a great technology that can reduce human error in manufacturing. It can be used to track the movement of components, semi-finished products, and finished products, and it can also be used to analyze the performance of individual employees and departments. It can also prevent the mixing of different styles or sizes of products.
While RFID has a number of benefits, there are still certain issues associated with its use in manufacturing. These include the cost and investment involved, as well as privacy and security issues. In addition, it’s important to note that RFID does not yet have any standardized standards, so the industry must continue to work on addressing these concerns.
How to Deploy RFID in Manufacturing Environments
Deploying RFID technology in a manufacturing environment, especially with a sophisticated system like Edgefinity IoT, requires a strategic and methodical approach.
The process begins with a comprehensive assessment of the manufacturing processes and the specific needs for RFID integration. First, RFID tags are selected based on the type of assets to be tracked, ensuring they are compatible with Edgefinity IoT’s capabilities. Next, RFID readers and antennas are strategically placed at key points in the production line and storage areas. These readers communicate with the RFID tags to capture data, enabling real-time tracking. The Edgefinity IoT system is then configured to process and manage the RFID data, allowing for easy access and analysis. Training for personnel on how to use the system is crucial for a successful deployment. Regular testing and monitoring ensure that the system operates effectively and any adjustments can be made promptly.
With Edgefinity IoT, manufacturers can seamlessly integrate RFID technology to enhance production tracking, streamline operations, and optimize inventory management for increased efficiency and productivity.




