Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has revolutionized various industries, and manufacturing is no exception. While passive RFID has been widely adopted for tracking and inventory management, active RFID takes the capabilities to a whole new level.
Active RFID tags are equipped with their own power source, allowing them to actively broadcast information, enabling real-time tracking and monitoring of assets. In this article, we will explore five key use cases where manufacturers can harness the power of active RFID technology to enhance their operations.
What is Active RFID?
RFID is a wireless tracking technology that uses radio signals to identify and monitor assets. Unlike passive RFID, which relies on power from the reader, active RFID tags have a built-in battery. This allows them to transmit signals continuously, enabling longer read ranges and real-time visibility.
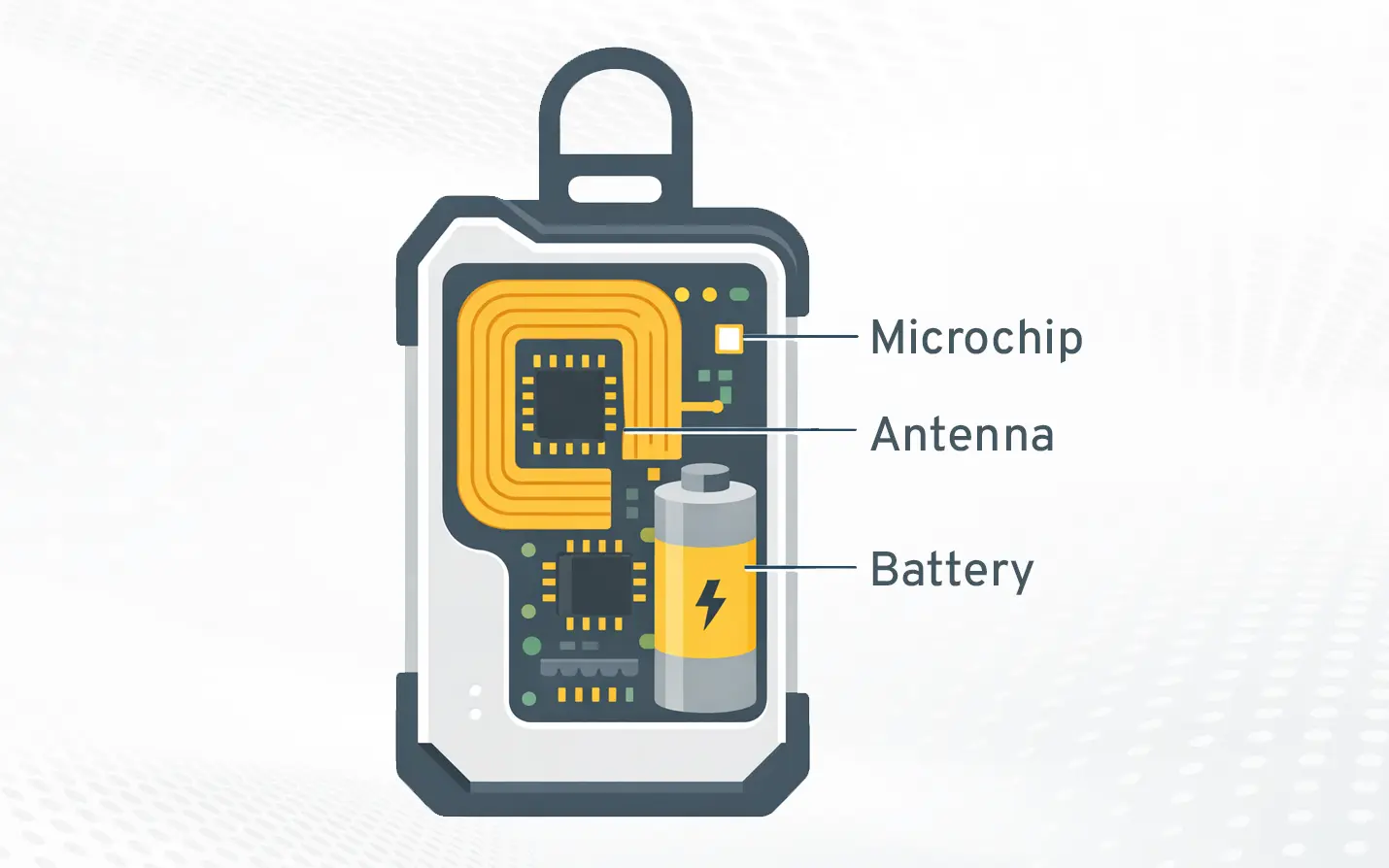
Because they are battery-powered, active RFID tags can send signals at set intervals or when triggered by specific events. Each tag typically includes a microchip, antenna, and battery working together to transmit data.
Active RFID is commonly used to track:
- High-value assets
- Mobile equipment and vehicles
- Shipping containers and yard assets
- Tools, machinery, or personnel
An active RFID system includes more than just tags. It also uses readers, antennas, and software to capture and manage location data. As tags broadcast their unique IDs, the system continuously updates asset location and status.
With long-range reads and constant updates, active RFID is ideal for environments that require real-time tracking, automated alerts, and zone-based visibility—such as warehouses, logistics yards, construction sites, and hospitals.
| Feature | Passive RFID | Active RFID |
|---|---|---|
| Power source | Powered by the RFID reader | Built-in battery |
| Read range | Short to medium (inches to ~30 ft) | Long range (100–300+ ft) |
| Tracking type | Event-based (scan points) | Continuous, real-time tracking |
| Tag cost | Low | Higher |
| Tag lifespan | Long (no battery) | Limited by battery life |
Active RFID Advantages Over Passive RFID
While passive RFID is ideal for many applications, active RFID offers unique advantages—especially in environments that demand constant updates, wide-area tracking, and real-time data visibility. Thanks to their built-in batteries and ability to transmit signals on their own, active RFID tags provide enhanced performance for dynamic asset management and monitoring.
Active RFID shines in large, complex environments—such as logistics yards, manufacturing plants, or hospitals—where you need to know where your assets are at all times.
Here’s how it delivers:
- Extended Ranges: Active RFID tags can be read over much greater distances than passive ones—often up to hundreds of feet. This makes them ideal for tracking moving vehicles, high-value tools, or mobile equipment across expansive facilities or outdoor areas.
- Continuous Communication: Active tags actively broadcast signals at regular intervals, providing real-time updates on location, status, or other relevant data. This continuous communication enables real-time tracking and monitoring of assets.
- Enhanced Data Transmission: Active RFID tags have the ability to transmit more data compared to passive tags. This allows for additional information such as temperature readings, data, or battery status to be included in the transmitted signals.
- Autonomous Operation: Active tags have their own power source, making them independent of external power. This allows them to operate autonomously, providing continuous tracking and monitoring capabilities without relying on an external power supply.
- Versatility and Customization: Active RFID technology can be customized to suit specific application requirements. Tags can be designed with various form factors, and battery life options to meet the specific needs of different industries or use cases.
Whether you’re managing fleet vehicles, tracking tools on a job site, or ensuring safety in a facility, active RFID provides the level of control and real-time insight that passive systems can’t match.
How Active RFID is Used
Active RFID is commonly used in environments that require real-time visibility, long read ranges, and continuous tracking. Because active tags broadcast signals using a built-in battery, they are well suited for monitoring high-value or highly mobile assets.
Common uses for active RFID include:
- Real-time asset tracking for vehicles, equipment, and high-value assets
- Yard and fleet management, including trailers, containers, and vehicles
- Work-in-process (WIP) tracking across large facilities or outdoor areas
- Personnel tracking for safety, security, and emergency response
- Worker safety monitoring, including zone-based alerts and restricted-area access
Some applications require continuous location updates and automated alerts, making active RFID the preferred choice over passive RFID. Understanding the differences between passive and active RFID helps ensure the right technology is used for the right tracking need.
Example of active tags from Sewio.
Active RFID Use Cases
Active RFID technology offers a wide range of specific use cases across various industries. Here are a few specific ways in which active RFID technology can be utilized:
Environmental Monitoring
Active RFID tags has the ability to monitor environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity. This helps improve the safety of assets and to prevent damage to equipment.
For example, a company that stores hazardous materials could use active RFID tags to monitor the temperature of the storage facility in order to ensure that the materials do not reach a dangerous or non-compliant level.
Tool and Equipment Management
Active tags can be attached to tools and equipment, allowing manufacturers to track their location and usage. This ensures that the right tools are available when and where they are needed, reducing downtime and improving productivity.
Manufacturers can also monitor tool maintenance schedules and receive alerts for preventive maintenance, ensuring optimal performance and prolonging the lifespan of expensive equipment.
Personnel Tracking and Safety
Active tags integrated into employee badges or PPE can enhance worker safety by monitoring their location within the manufacturing facility. In hazardous environments, such as construction sites or chemical plants, active tags can be used to ensure workers are in designated safe zones and to trigger alarms or alerts in case of emergencies. This application improves worker safety, enables quick response in critical situations, and helps manage evacuation procedures effectively.
Returnable Asset Tracking
In manufacturing operations that involve the use of returnable assets, such as containers, pallets, or racks, active RFID tags can be attached to these items to enable efficient tracking and management. By monitoring the movement of returnable assets in real time, manufacturers can optimize their utilization, reduce loss or theft, and ensure timely return and replenishment. This streamlines supply chain operations, minimizes the need for manual inventory checks, and improves asset visibility.
These specific applications highlight the versatility and value of active RFID technology in various industries.
By leveraging real-time tracking, monitoring, and data collection capabilities, manufacturers can streamline operations, improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance safety, and achieve better visibility and control over their assets and processes.
#MakeRFIDEasy
The RFID revolution is here. And CYBRA is at the forefront, ready to make the technology easier and more accessible than ever before.
Challenges
Deploying active RFID technology brings significant benefits, but it also comes with challenges that businesses must address. The higher cost of active tags, compared to passive RFID, can impact budgets, especially for large-scale deployments. Battery-powered tags require periodic maintenance or replacement, adding to operational complexity. Ensuring compatibility with existing systems and achieving seamless integration into workflows can also present technical hurdles.
Additionally, the increased range of active RFID may require careful configuration to avoid signal interference and maintain accuracy. Addressing these challenges upfront ensures a smoother implementation and maximized ROI.
Conclusion
In conclusion, active RFID technology offers organizations a wide range of applications to optimize their operations and enhance overall efficiency. By leveraging active RFID for asset tracking and management, inventory control, work-in-process tracking, quality control, and worker safety, manufacturers can gain real-time visibility, streamline processes, and make data-driven decisions.
With the ability to track and monitor assets, products, and personnel in real time, manufacturers can achieve greater operational excellence, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
How to Get Started with RFID
Getting started with active RFID begins with identifying your business needs. Pinpoint the assets or processes requiring real-time visibility, such as inventory management or equipment tracking.
Next, evaluate your environment to determine the ideal infrastructure, including tag types, readers, and software solutions. Partner with a provider experienced in active RFID to ensure seamless integration with your existing systems. Start small with a pilot program to test performance, train your team, and fine-tune configurations.
With careful planning, you can leverage active RFID to enhance visibility, reduce errors, and streamline operations effectively.
Interested in RFID?
An RFID tracking system can help organizations of all sizes improve their supply chain efficiency. Contact the CYBRA team to schedule a demo today.