RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology and Six Sigma methodologies represent powerful tools in the modern landscape of business process improvement. Each independently brings substantial benefits to organizations, but when integrated effectively, they can amplify operational efficiency, accuracy, and overall performance to new heights.
What is RFID Technology?
RFID technology revolves around the use of electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information that can be captured by RFID readers through radio waves, eliminating the need for direct line-of-sight contact. This ability to wirelessly and rapidly identify items has revolutionized inventory management, supply chain logistics, and asset tracking across various industries.
The core components of RFID systems typically include:
- Tags: These are attached to objects and contain a unique identifier and other relevant data.
- Readers: Devices that transmit and receive radio waves to communicate with RFID tags.
- Antennas: Transmit and receive signals between the reader and tags.
- Software: Manages and interprets data collected from RFID tags.
RFID tags come in two main types: active and passive. Active tags have their own power source and can transmit signals over longer distances, making them suitable for tracking high-value assets or vehicles. In contrast, passive tags rely on the reader’s electromagnetic field for power and are commonly used in inventory management due to their lower cost and smaller size.
The Role of Six Sigma in Process Improvement
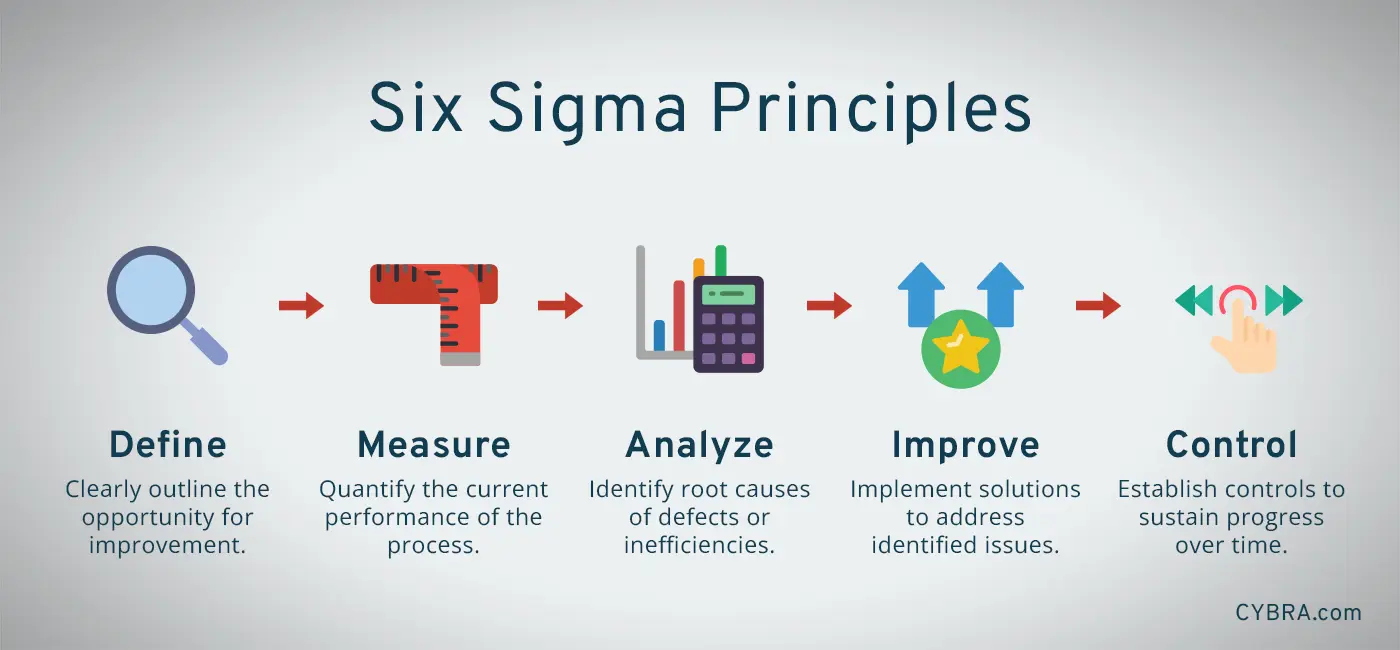
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology aimed at minimizing defects and improving processes by systematically identifying and removing sources of variation and waste. Developed initially by Motorola in the 1980s and popularized by companies like General Electric, Six Sigma emphasizes a structured approach involving five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control (DMAIC).
- Define: Clearly outline the problem or opportunity for improvement.
- Measure: Quantify the current performance of the process.
- Analyze: Identify root causes of defects or inefficiencies.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address identified issues.
- Control: Establish controls to sustain improvements over time.
Central to Six Sigma’s success is the use of statistical tools and techniques such as process mapping, Pareto analysis, hypothesis testing, and control charts. These tools help organizations make informed decisions based on data rather than assumptions, leading to more consistent and predictable outcomes.
Synergies Between RFID and Six Sigma
Integrating RFID technology with Six Sigma methodologies enhances process visibility, data accuracy, and decision-making capabilities across various operational domains:
- Improved Data Accuracy: RFID minimizes manual data entry errors by automating data capture and ensuring real-time visibility into inventory levels, asset locations, and production status. This accuracy supports reliable measurement and analysis phases in the Six Sigma DMAIC cycle.
- Enhanced Process Efficiency: By reducing the time and effort spent on manual tracking and inventory counts, RFID allows organizations to focus resources on value-added activities that drive process improvements. This efficiency aligns with Six Sigma’s goal of optimizing processes for maximum output with minimal waste.
- Faster Decision-Making: Real-time data provided by RFID enables quicker responses to changes in demand, supply chain disruptions, or production issues. This agility supports the Improve and Control phases of Six Sigma, where timely adjustments and continuous monitoring are critical to sustaining process improvements.
- Root Cause Analysis: RFID data can reveal patterns or anomalies that traditional methods might overlook, aiding in the identification of root causes during the Analyze phase of Six Sigma. For example, RFID data may highlight bottlenecks in workflow or inconsistencies in supply chain logistics that require further investigation.
- Process Standardization: RFID technology facilitates the standardization of processes by providing consistent and reliable data inputs. This standardization is essential for implementing and maintaining control measures as part of the Six Sigma methodology, ensuring that improvements are sustained over the long term.
Use Cases and Real-World Applications
Numerous industries have successfully integrated RFID technology with Six Sigma principles to achieve significant improvements in operational efficiency and customer satisfaction:
- Manufacturing: Implementing RFID-enabled systems for real-time inventory replenishment, reducing stockouts and improving production flow.
- Retail: Enhancing supply chain visibility and inventory accuracy, leading to improved on-shelf availability and reduced carrying costs.
- Healthcare: Utilizing RFID tags for tracking medical equipment and patient records, minimizing errors and improving asset utilization.
- Logistics: Optimizing warehouse operations through RFID-enabled picking processes, reducing fulfillment times and labor costs.
#MakeRFIDEasy
The RFID revolution is here. And CYBRA is at the forefront, ready to make the technology easier and more accessible than ever before.
Challenges and Considerations
While the integration of RFID technology with Six Sigma offers substantial benefits, organizations must navigate potential challenges:
- Cost: Initial investment in RFID infrastructure and integration with existing systems can be significant, requiring careful cost-benefit analysis.
- Change Management: Adoption of new technologies and methodologies may face resistance from employees accustomed to traditional processes.
- Data Security: Ensuring the integrity and security of RFID data to protect against unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Compatibility: Compatibility with existing IT infrastructure and systems, requiring thorough planning and integration efforts.
Leveraging RFID into Your Six Sigma Endeavors
By leveraging RFID’s capabilities for real-time data capture and automation with Six Sigma’s disciplined approach to process improvement, organizations can achieve higher efficiency, lower costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
CYBRA’s RFID application, Edgefinity IoT, can significantly enhance inventory tracking and align with Six Sigma principles by providing real-time visibility and data-driven insights into inventory management processes.
Utilizing RFID and other technologies, Edgefinity IoT enables precise tracking of inventory locations and movements, reducing errors and inefficiencies. By continuously collecting and analyzing data, businesses can identify patterns and root causes of inventory discrepancies, supporting the Six Sigma principle of data-driven decision making.
Interested in RFID?
An RFID tracking system can help organizations of all sizes improve their supply chain efficiency. Contact the CYBRA team to schedule a demo today.
















