RFID and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) are two powerful technologies used to track assets, monitor movement, and improve visibility across physical environments—but they serve different purposes and excel in different scenarios. While RFID is often used for identification, validation, and high-volume tracking, BLE focuses on real-time location and proximity awareness.
In this article, we’ll compare RFID and BLE side by side, breaking down how each technology works, where they deliver the most value, and how to choose the right option for your tracking needs.
RFID
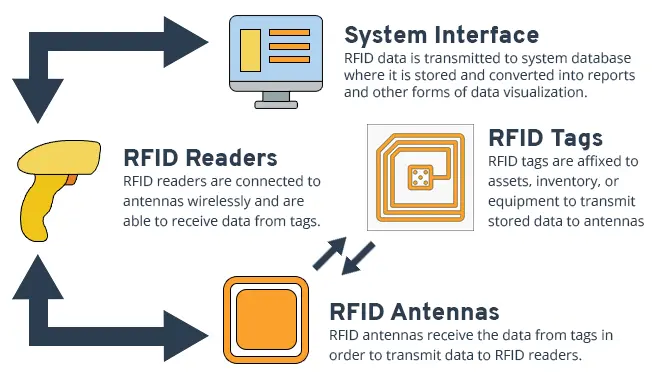
Harnessing radio waves for identification is what RFID is all about. This technology is an established form of wireless communication used for identification and tracking purposes. RFID systems consist of three main components: RFID tags, readers, and a backend database or software for data management.
Usually, RFID tags are very small, passive devices that can be attached to objects, products, or assets. These tags contain a microchip and an antenna, and they do not require a power source of their own. Instead, they draw power from the radio waves emitted by RFID readers when they come into the read range. When a reader emits radio frequency signals, the RFID tag responds by transmitting its unique identification data, allowing the reader to identify and track the tagged item.
RFID technology has been growing in popularity and is highly effective in scenarios where a large number of items need to be identified rapidly. In industries like logistics and supply chain management, RFID enables real-time tracking of goods, optimizing inventory management, and reducing errors. It is also widely used in access control, asset tracking, and in retail for inventory monitoring and loss prevention.
RFID Use Cases
RFID supports a wide range of use cases across industries by enabling accurate, automated identification and tracking. From inventory and asset management to compliance and workflow optimization, RFID helps organizations reduce manual effort, improve visibility, and make faster, data-driven decisions.
Inventory Control
RFID is extensively used in supply chain and logistics operations to track and manage inventory throughout the entire distribution process. Tags attached to products or packages allow for real-time monitoring, reducing errors, improving visibility, and optimizing inventory levels.
Retail and Point-of-Sale (POS)
In the retail sector, RFID tags on products streamline inventory management and enhance the shopping experience. Retailers can use RFID to perform accurate and rapid stock counts, reducing out-of-stock situations and improving shelf replenishment.
Asset Tracking
RFID is deployed for asset tracking in various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and construction. Companies can efficiently manage and locate valuable assets, equipment, and tools using RFID tags attached to these items.
Access Control and Security
RFID-based access control systems provide secure and convenient entry management for buildings, offices, and restricted areas. Employees and authorized personnel can use RFID cards or badges to gain access to specific locations.

RFID ROI Calculator
Take the guesswork out of your investment with our ROI calculator. See potential savings and discover how RFID can enhance operations across industries.
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy)
The Power of Proximity and Interactivity BLE, or Bluetooth Low Energy, is a wireless communication technology that operates on the same principle as traditional Bluetooth but with lower energy consumption. BLE is designed for applications where data transfer is required over short distances with minimal power usage.
BLE-enabled devices, like smartphones or beacons, can communicate with one another in close proximity using Bluetooth signals. Bluetooth beacons are small, battery-operated devices that continuously broadcast signals containing unique identification data. When a compatible device, such as a smartphone or a specialized BLE reader, comes into range, it can detect these signals and receive the data transmitted by the beacon.
BLE technology excels in applications that require proximity-based interactions and location-based services. In retail, BLE beacons enable retailers to offer personalized promotions, notifications, and product information to customers’ smartphones based on their proximity to specific store sections or products. BLE is also used in asset tracking and indoor navigation, where it provides precise location data within buildings or facilities.
BLE Use Cases
This technology excels in use cases that require continuous location awareness and proximity-based interactions. By broadcasting signals at regular intervals, BLE delivers real-time tracking, indoor positioning, and location-based alerts—making it ideal for environments where knowing where something is matters as much as what it is.
Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
BLE is a fundamental technology in the IoT ecosystem. It enables seamless communication between IoT devices and smartphones or gateways, supporting direct data and command exchange. Manufacturers use BLE in smart home devices, wearables, health monitoring systems, and other connected IoT solutions.
Proximity Marketing and Beacons
BLE beacons are small devices that broadcast signals containing unique identification data to nearby smartphones or devices. This enables proximity-based marketing, providing users with location-based content, offers, and information when they are in close proximity to the beacon. Proximity marketing is widely used in retail stores, museums, airports, and other public spaces.
Indoor Navigation and Wayfinding
BLE is utilized for indoor positioning systems that enable accurate navigation within large indoor spaces like shopping malls, airports, or exhibition centers. BLE beacons placed strategically throughout the venue interact with users’ smartphones, providing real-time directions and wayfinding assistance.
| Feature | RFID | BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary purpose | Identification and tracking | Real-time location and proximity tracking |
| Power source | Passive (reader-powered) or active (battery) | Battery-powered |
| Read range | Passive: short–medium | Active: long | Medium to long |
| Tracking method | Event-based (checkpoints, portals) | Continuous or near-real-time |
| Tag/beacon cost | Low (passive), higher (active) | Higher than passive RFID |
| Infrastructure | RFID readers and antennas | BLE beacons + gateways or receivers |
| Data transmission | Responds when read (passive) or broadcasts (active) | Periodic broadcasting |
| Battery maintenance | None (passive) / required (active) | Required |
| Best suited for | Inventory, assets, compliance, validation | Location tracking, proximity detection, wayfinding |
| Typical environments | Warehouses, manufacturing, retail, logistics | Campuses, hospitals, offices, large facilities |
| Scalability | Excellent for high-volume items | Better for lower volumes of high-value assets |
RFID vs. BLE: A Comparative Analysis
While both RFID and BLE enable wireless identification and tracking, they serve different use cases. One key difference is range: RFID typically supports longer read distances, while BLE operates at shorter ranges and excels in proximity-based applications.
Power requirements also differ. RFID tags are often passive and battery-free, making them cost-effective for long-term tracking, while BLE beacons rely on batteries and require periodic maintenance.
RFID also supports simultaneous identification of many items, making it ideal for inventory-heavy environments. BLE, by contrast, enables interactive, proximity-based experiences—often through smartphones—making it well suited for customer engagement and location-aware applications.
Final Analysis
RFID and BLE are powerful wireless technologies that have revolutionized various industries by enabling efficient identification, tracking, and communication. While RFID excels in long-range, high-volume item tracking scenarios, BLE is designed for proximity-based applications and interactive customer experiences.
Understanding the unique advantages and use cases of both technologies allows businesses to harness their potential to optimize processes, enhance customer engagement, and drive innovation across diverse industries in the age of smart connectivity.
Interested in RFID?
An RFID tracking system can help organizations of all sizes improve their supply chain efficiency. Contact the CYBRA team to schedule a demo today.