In today’s interconnected and globalized world, the transportation and storage of temperature-sensitive goods, such as perishable foods, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines, have become essential but challenging tasks. Ensuring that these products maintain the required temperature throughout their journey from production to consumption is critical to preserving their quality and efficacy. Cold chain management, a complex process involving the monitoring and control of temperature-sensitive products, plays a crucial role in this regard. One technology that has revolutionized cold chain management is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). In this article, we will explore how RFID helps with cold chain management and its impact on various industries.
Understanding the Cold Chain:
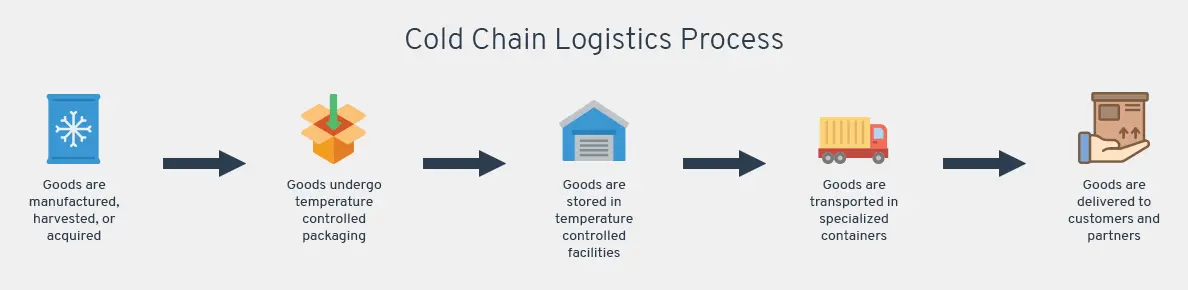
The cold chain is a supply chain process that involves the transportation, storage, and handling of temperature-sensitive products within a specified temperature range. This range is typically between -25°C to +8°C for frozen products and +2°C to +8°C for refrigerated products. Failure to maintain the required temperature during any stage of the cold chain can result in product spoilage, reduced potency of medicines, or even health risks to consumers.
The Role of RFID in Cold Chain Management:
RFID technology utilizes radio frequency signals to transfer data between a tag and a reader. The RFID tag is attached to the product or packaging, and the reader collects information from the tag, such as the product’s temperature, location, and other relevant data. This technology offers several key advantages that significantly enhance cold chain management processes:
- Real-Time Temperature Monitoring: RFID tags can continuously monitor the product’s temperature. The real-time data is transmitted to the reader at various points along the cold chain journey. This allows stakeholders to identify temperature fluctuations or deviations immediately, enabling them to take prompt corrective action before the product’s quality is compromised.
- Enhanced Traceability: RFID tags provide unique identification codes for each product or shipment. This level of traceability allows stakeholders to track individual items throughout the supply chain accurately. By knowing the product’s exact location at any given time, cold chain managers can detect potential delays or deviations and reroute shipments to avoid temperature-sensitive issues.
- Data Accuracy and Automation: RFID systems reduce the risk of human error and increase data accuracy compared to manual recording processes. The automation of data collection and monitoring streamlines cold chain management, providing reliable information for decision-making and compliance reporting.
- Alerts and Notifications: RFID systems can be configured to trigger alerts and notifications when temperature thresholds are breached or when there are other critical issues. This proactive approach allows stakeholders to address potential problems before they escalate, preventing product spoilage and losses.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Many industries, such as pharmaceuticals and food, have stringent regulations regarding temperature-controlled transportation and storage. RFID technology helps ensure compliance with these requirements by providing detailed, auditable records of temperature conditions throughout the cold chain journey.
- Reduced Losses and Waste: By maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive products, RFID contributes to a significant reduction in losses and waste. This is particularly crucial in industries like healthcare, where temperature variations can render life-saving medications ineffective.
Applications of RFID in Cold Chain Management
RFID in cold chain is applicable across numerous industries:
- Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare: In the pharmaceutical industry, RFID plays a vital role in ensuring the efficacy of medicines and vaccines. From manufacturing facilities to distribution centers and pharmacies, RFID helps monitor temperature-sensitive drugs at every stage of the supply chain. This level of control ensures that medications reach patients in optimal condition, promoting better patient outcomes.
- Food and Beverage Industry: The food and beverage industry relies heavily on the cold chain to preserve the freshness and safety of perishable products. RFID technology enables food producers, distributors, and retailers to track temperature-sensitive items accurately. It helps prevent food spoilage, reduces foodborne illnesses, and extends the shelf life of products.
- Biotechnology and Life Sciences: In the biotechnology and life sciences sectors, RFID assists in managing temperature-sensitive biological samples, tissues, and specimens. Maintaining the integrity of these materials is crucial for research, diagnostics, and medical advancements.
- Chemical and Industrial Products: Certain chemical and industrial products require specific temperature conditions to maintain stability and prevent hazardous reactions. RFID monitoring ensures that these products are transported and stored safely, minimizing the risk of accidents and environmental contamination.
Challenges and Considerations
While RFID offers numerous benefits to cold chain management, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Cost: Implementing RFID technology can involve initial setup costs, including tags, readers, and software integration. However, the long-term benefits in terms of efficiency, reduced losses, and regulatory compliance often outweigh the initial investment.
- Compatibility and Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different RFID systems and devices is essential, especially when multiple stakeholders are involved in the supply chain. Standardization efforts help address this challenge and promote seamless data exchange.
- Data Security and Privacy: Cold chain data, especially in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors, is sensitive and requires robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Training and Adoption: Proper training of personnel is necessary to ensure the successful adoption of RFID technology. Stakeholders must understand how to use the technology effectively and interpret the data provided by the RFID system.
Conclusion
RFID technology has revolutionized cold chain management by providing real-time temperature monitoring, enhanced traceability, data accuracy, and automation. It has become a game-changer in industries where temperature-sensitive products are critical to human health and safety. By leveraging the power of RFID, stakeholders in pharmaceuticals, food, biotechnology, and other sectors can ensure the integrity of their products, reduce losses, comply with regulations, and ultimately provide consumers with high-quality and safe goods. As technology continues to advance, we can expect RFID to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of cold chain management, leading to increased efficiency and sustainability in supply chain operations.
Interested in RFID?
An RFID tracking system can help organizations of all sizes improve their supply chain efficiency. Contact the CYBRA team schedule a demo today.