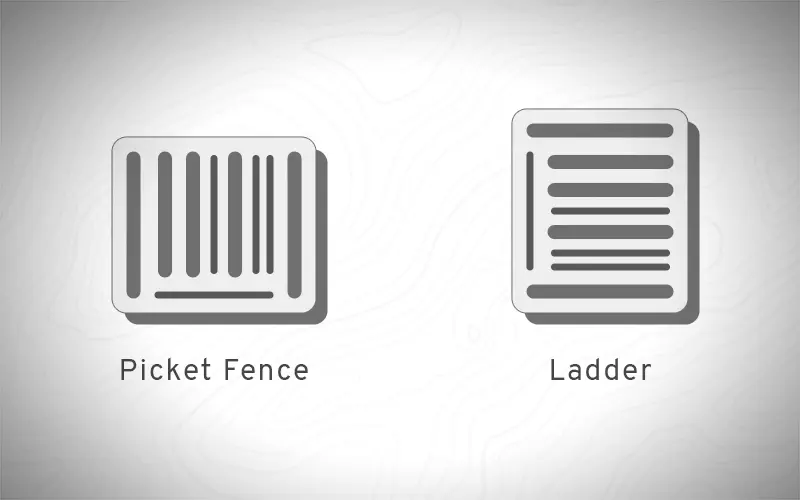
The orientation of the barcode can significantly impact its readability and the efficiency of the scanning process. The two common orientations are the “picket fence” and “ladder” orientations. Each has distinct characteristics and is suitable for different applications, depending on the scanning environment and the type of scanner used.
Picket Fence Barcode Orientation
The picket fence orientation, also known as the horizontal orientation, positions the barcode’s lines like a series of vertical pickets in a fence. This is the most commonly used orientation for barcodes, especially in retail environments.
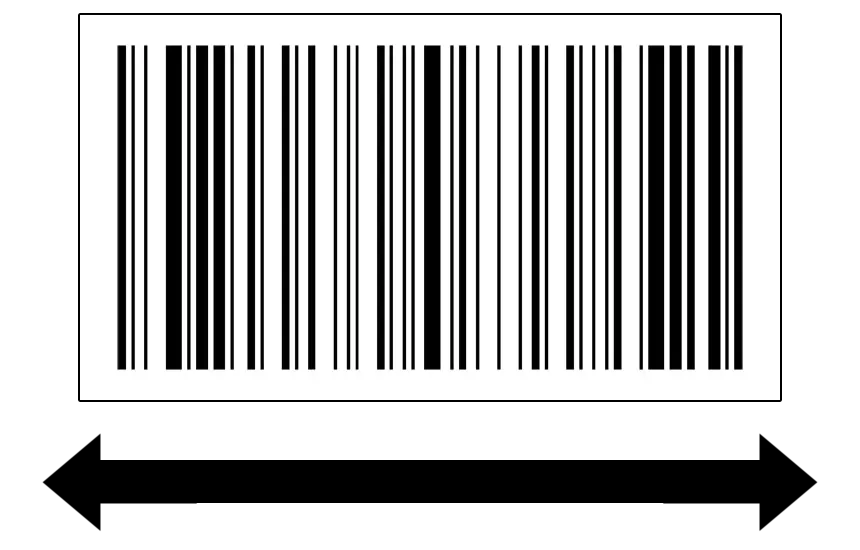
Picket Fence Barcode
The key benefits of the picket fence orientation include:
- Ease of Scanning: Most handheld scanners are designed to read horizontally oriented barcodes more efficiently. This makes the picket fence orientation ideal for point-of-sale systems where speed and accuracy are critical.
- Compatibility with Conveyor Systems: In automated systems, such as those used in logistics and manufacturing, the picket fence orientation is often preferred because it aligns well with the direction of movement on conveyor belts.
- Standardization: Many standard barcode formats, such as UPC and EAN codes used in retail, are traditionally printed in the picket fence orientation, ensuring broad compatibility across various systems.
Ladder Barcode Orientation
The ladder orientation, or vertical orientation, arranges the barcode’s lines horizontally, resembling the rungs of a ladder. This orientation is less common but has specific applications where it is particularly beneficial:
- Limited Space: In environments where there is limited horizontal space, such as on small or cylindrical products, the ladder orientation can be more practical. It allows for the barcode to fit in narrower spaces where a horizontally oriented barcode might be too wide.
- High-Speed Scanning: Some industrial settings use line-scan cameras or fixed-position scanners that scan barcodes as they move past the scanner. In these scenarios, a ladder orientation can provide a more reliable read because the scanning motion aligns with the barcode’s orientation.
- Printing Considerations: When barcodes are printed in environments with constraints on the direction of print, such as on certain packaging lines, the ladder orientation can be more efficient and prevent distortion that could occur if the barcode were printed horizontally.
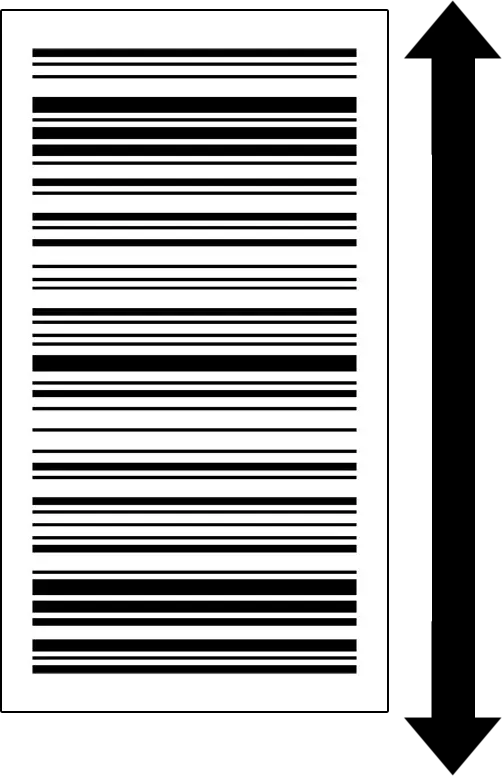
Ladder Barcode
Choosing the Right Orientation
Selecting between picket fence and ladder barcode orientations depends on the specific requirements of the application. Factors to consider include the type of scanner being used, the available space on the product, the speed and direction of the scanning process, and the industry standards that apply.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between picket fence and ladder barcode orientations and their respective advantages can help businesses optimize their barcode systems for better efficiency and accuracy. Whether in retail, logistics, manufacturing, or healthcare, choosing the appropriate orientation is a crucial step in ensuring seamless barcode scanning and data capture.
Better Labeling, Faster Printing.
Ensure every label is accurate, compliant, and printed without delays. Discover how CYBRA’s barcode and printing solutions streamline operations and eliminate errors.