Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology enables automatic identification and tracking of objects using radio waves—without requiring line-of-sight scanning. Unlike barcodes, RFID systems can read multiple items simultaneously, capture data in real time, and operate in demanding environments such as warehouses, hospitals, and manufacturing facilities.
Understanding how RFID technology works starts with its core components and how they interact.
The Core Components of an RFID System
An RFID system consists of four primary elements:
1. RFID Tags
RFID tags are small electronic devices attached to items, assets, or containers. Each tag contains:
- A microchip that stores a unique identifier (and sometimes additional data)
- An antenna that transmits data via radio waves
RFID tags come in several forms:
- Passive RFID tags – powered by the reader’s signal (most common)
- Active RFID tags – battery-powered, longer read ranges
- Semi-passive (battery-assisted) tags – hybrid approach
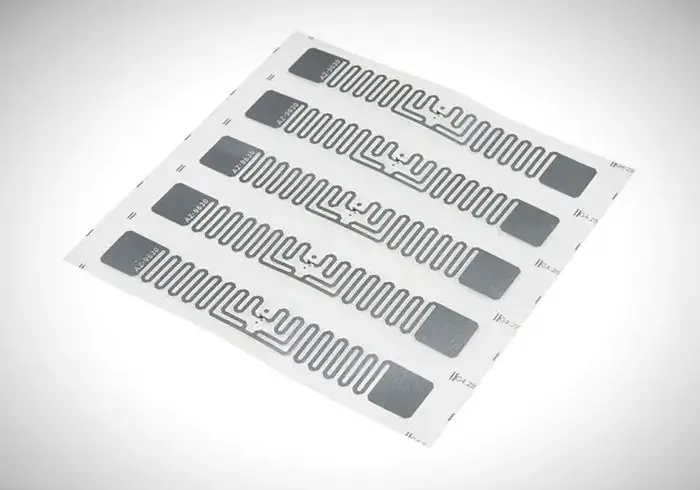
2. RFID Readers
RFID readers (also called interrogators) transmit radio frequency signals that activate RFID tags within range. When a tag responds, the reader captures the data and sends it directly to connected software systems.
Readers can be:
- Fixed (dock doors, portals, ceilings)
- Handheld
- Embedded in printers, kiosks, or mobile devices
3. RFID Antennas
Antennas control the read zone and determine how signals are transmitted and received. Antenna design affects read range, accuracy, and performance—especially around metal, liquids, or dense environments.
Teams deploy multiple antennas to cover large areas or define specific read zones.
4. RFID Software & Middleware
RFID software collects, filters, and processes tag data. It connects RFID hardware to enterprise systems such as:
- WMS (Warehouse Management Systems)
- ERP platforms
- Asset management or IoT dashboards
This layer turns raw RFID reads into actionable events like “item entered zone,” “asset moved,” or “inventory verified.”
Start Using RFID with Minimal Investment →
CYBRA’s RFID starter kit built for simplicity. Perfect for small projects or proof-of-concepts, EdgeMicro lets you bring RFID into your supply chain with less cost, less risk, and faster results.
How RFID Data Is Captured (Step by Step)
- The RFID reader emits a radio signal
- RFID tags within range are energized or triggered
- Tags transmit their stored data back to the reader
- The reader forwards the data to software
- Systems log, analyze, and act on the information in real time
Because RFID does not require line of sight, hundreds of tags can be read simultaneously—even through packaging or containers.
RFID Frequencies and Read Ranges
RFID operates across different frequency bands:
- LF (Low Frequency): Short range, animal ID, access control
- HF (High Frequency / NFC): Contactless payments, badges
- UHF (Ultra-High Frequency): Long-range tracking, inventory, supply chain
- Microwave: Specialized active tracking use cases
UHF RFID is the most widely used in enterprise environments due to its speed, range, and scalability.
Final Thoughts
RFID technology works by combining tags, readers, antennas, and software into a connected system that automatically identifies and tracks physical items using radio waves. By removing manual scanning and providing real-time visibility, RFID enables faster operations, higher accuracy, and smarter decision-making across modern enterprises.
As RFID continues to evolve—especially when paired with IoT, AI, and analytics—it is becoming a foundational technology for digital transformation and Industry 4.0 initiatives.
Interested in RFID?
An RFID tracking system can help organizations of all sizes improve their supply chain efficiency. Contact the CYBRA team to schedule a demo today.